In addition to developing apps that allow patients to track their lifestyle habits—exercise, diet, sleep patterns, etc—mHealth is also promising in its potential to engage patients in their general health information. Specifically, in the information that is stored in hospital health records. A play on EHRs, Mana Health has developed “a patient portal solution that has been designed for today’s consumer.”
Mana Health is a New York startup that won the opportunity to design the patient portal for the New York eHealth Collaborative, a non-profit organization that works to improve health care for New Yorkers through the development and establishment of electronic health records. Mana Health recently designed an interface that facilitates the sharing of patient data around the state, not only between hospitals, but also from hospital-to-patient. The endeavor is unique because it is not contained in a single healthcare system, but rather will pull information from across the state and consolidate it in a user-friendly “patient portal” platform.
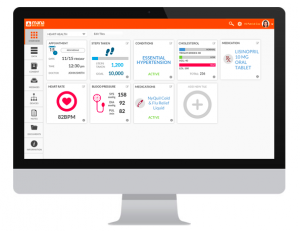
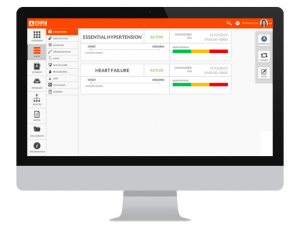
One of the best features of the program, at least in my opinion, is how user-friendly the interface appears to be. While existing electronic medical records (such as Epic) are filled with numbers and abbreviations, Mana Health’s platform is truly geared towards the patient and offers streamlined graphics that illustrate the patient’s relevant health information.
Mana Health’s platform transforms the complex electronic health record into a personal health record that allows patients easy access to their information: “unlike the clunky PHRs of days past, they said they wanted something that a typical consumer would feel comfortable using.” Their concern for user-centered designs is something that all mHealth developers should strive to emulate. The liberal use of color-coded graphics is a simple way to increase the scope of users, especially to those who may have low health literacy and will serve to benefit from the image-based layout.
As mHealth advances, there are many issues that will continue to spring up. I have addressed several of these in past blog posts—addressing low health literacy, accessing hard-to-reach populations, funding mHealth endeavors—and the creation of user-friendly platforms is yet another point of serious consideration. mHealth is a direct product of creativity and innovation, and these driving forces should not stop at the development of the idea, but carry over into the details of its execution.
http://www.mhealthnews.com/news/new-patient-portals-bring-mobility-hix?page=0
http://mana-health.com
http://nyehealth.org/about-nyec/